There are three primary functions of roots include
- absorbing (and storing) nutrients,
- acquiring dissolved minerals and water from the soil, and
- securing the plant in the soil.
Perennial plant root systems continue to perform these activities, at least on a limited basis, through winter; resuming new root growth each season. There are also specialized types of root systems that enable climbing plants and epiphytes to attach to rocks, bark, and other non-soil substrates.
Bare root perennials display four different types of root systems:
 Fibrous roots are composed of a mass of profusely branched
roots with many side rootlets, often with no main taproot. These roots grow
from the same cells as the plant stem and are generally finer than tap roots
and form a dense mat beneath the plant. With no main or taproot, fibrous root
systems can often be divided. Grass, tickseed, daylilies, hostas and Achillea
are typical example of fibrous systems.
Fibrous roots are composed of a mass of profusely branched
roots with many side rootlets, often with no main taproot. These roots grow
from the same cells as the plant stem and are generally finer than tap roots
and form a dense mat beneath the plant. With no main or taproot, fibrous root
systems can often be divided. Grass, tickseed, daylilies, hostas and Achillea
are typical example of fibrous systems.
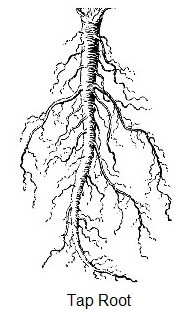 Taproot is the main descending root of a plant, often with
little branching. In the taproot system, the primary root continues to grow
into one main trunk with smaller root branches emerging from its sides. Division
is generally not recommended. Taproots can be modified to serve as carbohydrate
storage, as seen in carrots or beets, or to grow deeply in search of water as
those found in mesquite, poison ivy, Gypsophila or Platycodon.
Taproot is the main descending root of a plant, often with
little branching. In the taproot system, the primary root continues to grow
into one main trunk with smaller root branches emerging from its sides. Division
is generally not recommended. Taproots can be modified to serve as carbohydrate
storage, as seen in carrots or beets, or to grow deeply in search of water as
those found in mesquite, poison ivy, Gypsophila or Platycodon.
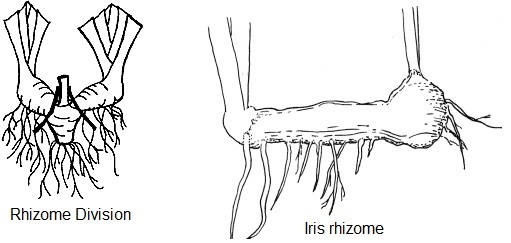 A rhizome root system is a horizontal underground stem, with
slender or swollen stems that branch close to the soil surface. This type of
root system produces roots, stems, leaves and flowers along its length and
apex. When dividing, each division
should retain a few inches of the rhizome and one fan of leaves that has been
trimmed back by one half. Cut out and discard rhizome sections that have been
damaged by insects or disease. Rhizomes should be replanted with the top
showing just above soil level. Tall Bearded Iris are examples.
A rhizome root system is a horizontal underground stem, with
slender or swollen stems that branch close to the soil surface. This type of
root system produces roots, stems, leaves and flowers along its length and
apex. When dividing, each division
should retain a few inches of the rhizome and one fan of leaves that has been
trimmed back by one half. Cut out and discard rhizome sections that have been
damaged by insects or disease. Rhizomes should be replanted with the top
showing just above soil level. Tall Bearded Iris are examples.
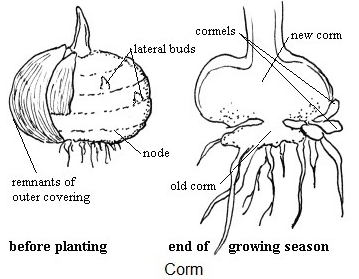
The fourth type of root system is the Crom, a solid underground, bulb-like portion of the stem of a plant that consists of fleshy tissues and bearing roots at the base. For example Crocosmia